Green Construction Materials
Cement stands as the most vital binding agent in concrete and a fundamental construction material used worldwide. Yet, its production contributes about 8% to the world's carbon dioxide emissions. Green construction materials are environment friendly alternatives to construction building materials. These materials can be selected based on their sustainability, energy efficiency, and minimal environment impact throughout their lifecycle.
Slag Cement for Stronger, Greener Construction
Slag Cement, also known as ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBS) is a byproduct of steel manufacturing process and is considered a green construction material due to its environmental benefits. It has been found to be a sustainable alternative that revolutionizes the concrete production. The process requires less than a fifth of the energy and produces less than a tenth of the carbon dioxide emissions, making it a more environmentally friendly. Slag cement (SC) offers a compelling alternative to traditional Portland cement, providing sustainable, durable, and high-performance solutions for the construction industry.
Key to Unlock Full Potential of Slag Cement
The particle size of slag cement plays a crucial role in determining its performance and overall effectiveness in concrete applications. Controlling the particle size helps industrialists in further optimizing the performance, workability, and durability of concrete mixes, ultimately leading to more sustainable and resilient construction materials. Managing particle size typically between 10μm and 20μm not only saves energy and costs, but also influences packing density and water demand, which is a crucial factor for an efficient construction material.
HORIBA: Pioneering Precision Solutions for Construction Industry
HORIBA Partica LA-960V2 laser diffraction particle size distribution analyser plays a significant role in optimizing the performance of slag cement by providing precise and efficient particle size analysis. The system is esteemed for its precision and accuracy, contingent upon adhering to appropriate sample preparation and measurement protocols. Here we illustrated (Figure 1) the comparison of particle size distributions acquired for the slag cement sample under both wet and dry conditions. The consistent data obtained regardless of the mode employed fosters confidence in the generated particle size data, empowering informed decision-making in cement production and research endeavours.
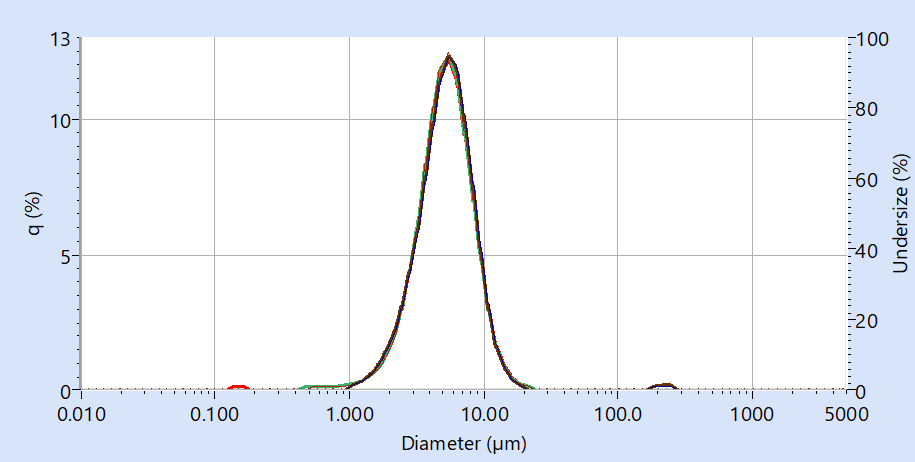
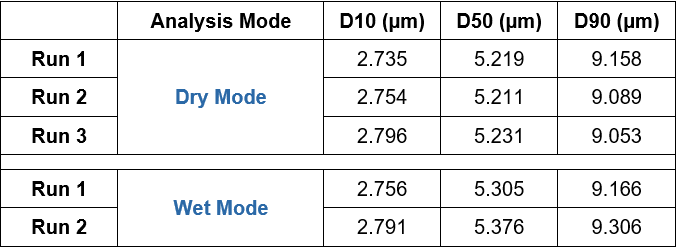
Automated data analysis software simplifies the interpretation of particle size distribution data extracted from the graph, facilitating researchers and engineers in deriving significant insights. Table 1 shows results from repeat runs of slag cement sample in both wet and dry mode showcasing the LA960 system's outstanding performance in data repeatability and reproducibility. Moreover, the system follows industry regulatory guidelines ensuring standardized, reliable and scientifically recognized method that comply with ISO13320.
Power of the Japanese Technology
The versatility of HORIBA LA960V2 makes it suitable for day-to-day monitoring of particle size distribution in various industrial applications, typically containing a broad range of particle sizes. Rapid analysis time is advantageous for quality control and process optimization in the production facilities, where timely particle size data is essential for maintaining product consistency and performance. Overall, laser diffraction is a valuable tool for the particle sizing of slag cement, offering speed, accuracy, and versatility for analysing the complex particle size distribution of this important construction material.
Leave a Comment
Comments
Ms. Jyoti Pant This is a very informative article!
Posted on Jan 20, 2025